785 lines
22 KiB
Markdown
785 lines
22 KiB
Markdown
# STL源码剖析之vector
|
||
|
||
## 0.导语
|
||
|
||
vector的数据安排以及操作方式,与array非常相似。两者的唯一差别在于空间的运用的灵活性,array是静态的,一旦配置了就不能改变,而 vector是动态空间,随着元素的加入,它的内部机制会自行扩充空间以容纳新元素。下面一起来看一下vector的"内部机制",怎么来实现空间配置策略的。
|
||
|
||
## 1.vector
|
||
|
||
在`_Vector_base`中开头有两行比较难理解,下面一个一个分析:
|
||
|
||
### 1.1 _Tp_alloc_type
|
||
开头处定义:
|
||
```
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在`__gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits`中:对应文件为:`ext/alloc_traits.h`
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Tp>
|
||
struct rebind
|
||
{ typedef typename _Base_type::template rebind_alloc<_Tp> other; };
|
||
```
|
||
等价于
|
||
```
|
||
typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other
|
||
```
|
||
等价于:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typename _Base_type::template rebind_alloc<_Tp>
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
而`_Base_type`是:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef std::allocator_traits<_Alloc> _Base_type;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
所以上述等价于:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typename std::allocator_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind_alloc<_Tp>
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
继续到`allocator_traits`中寻找
|
||
|
||
找到了:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Up>
|
||
using rebind_alloc = allocator<_Up>;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
于是:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
std::allocator_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind_alloc<_Tp>
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
等价于:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
allocator<_Tp>
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
> 小结
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
等价于:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef allocator<_Tp> _Tp_alloc_type
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 1.2 pointer
|
||
|
||
而`pointer`:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
等价于:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<allocator<_Tp>>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
根据下面两行:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef std::allocator_traits<_Alloc> _Base_type;
|
||
typedef typename _Base_type::pointer pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
又等价于:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
typedef std::allocator_traits<_Alloc>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在`allocator_traits`中找到下面:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
/**
|
||
* @brief The allocator's pointer type.
|
||
*
|
||
* @c Alloc::pointer if that type exists, otherwise @c value_type*
|
||
*/
|
||
typedef __pointer pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
注释中说了如果存在就是`Alloc::pointer`,否则为` value_type *`。
|
||
|
||
> 小结
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
// 或者
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<allocator<_Tp>>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
等价于
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
/**
|
||
* @brief The allocator's pointer type.
|
||
*
|
||
* @c Alloc::pointer if that type exists, otherwise @c value_type*
|
||
*/
|
||
typedef __pointer pointer;
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果存在`_Tp_alloc_type::pointer`也就是`allocator<_Tp>`存在就是`allocator<_Tp>::pointer`,
|
||
|
||
这个看`allocator.h`源码:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef _Tp* pointer;
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
否则为` value_type*`。而`value_type`为:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef typename _Alloc::value_type value_type;
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
所以`value_type*`推导出为:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
_Tp::value_type*
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### 1.3 vector的内存管理
|
||
|
||
`_Vector_base`中有一个**内存管理器**`_Vector_impl`类,该结构体继承`allocator`(根据上述1.1等价条件得出)。
|
||
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
|
||
struct _Vector_base {
|
||
//__alloc_traits -> allocator_traits
|
||
// typedef allocator<_Tp> _Tp_alloc_type
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template
|
||
rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type;
|
||
// _Tp::value_type* or _Tp*
|
||
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type>::pointer
|
||
pointer;
|
||
|
||
struct _Vector_impl
|
||
: public _Tp_alloc_type {
|
||
pointer _M_start; // 使用空间起始位置
|
||
pointer _M_finish; // 使用空间结束位置
|
||
pointer _M_end_of_storage; // 可使用空间结束位置
|
||
|
||
_Vector_impl()
|
||
: _Tp_alloc_type(), _M_start(0), _M_finish(0), _M_end_of_storage(0) {}
|
||
|
||
_Vector_impl(_Tp_alloc_type const &__a)
|
||
|
||
// vector数据交换,只交换内存地址,不交换数据
|
||
void _M_swap_data(_Vector_impl &__x)
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{
|
||
std::swap(_M_start, __x._M_start);
|
||
std::swap(_M_finish, __x._M_finish);
|
||
std::swap(_M_end_of_storage, __x._M_end_of_storage);
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
|
||
// 前面我们知道_Vector_impl继承自allocator分配器,而这个又是_Tp_alloc_type,所以这里返回的就是_M_impl的基类。
|
||
_Tp_alloc_type &
|
||
_M_get_Tp_allocator()
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return *static_cast<_Tp_alloc_type *>(&this->_M_impl); }
|
||
|
||
const _Tp_alloc_type &
|
||
_M_get_Tp_allocator() const
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return *static_cast<const _Tp_alloc_type *>(&this->_M_impl); }
|
||
|
||
allocator_type // 获取传递进来的分配器
|
||
get_allocator() const
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return allocator_type(_M_get_Tp_allocator()); }
|
||
|
||
_Vector_base()
|
||
: _M_impl() {}
|
||
|
||
_Vector_base(const allocator_type &__a)
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
: _M_impl(__a) {}
|
||
|
||
_Vector_base(size_t __n)
|
||
: _M_impl() { _M_create_storage(__n); }
|
||
|
||
_Vector_base(size_t __n, const allocator_type &__a)
|
||
: _M_impl(__a) { _M_create_storage(__n); }
|
||
|
||
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
|
||
_Vector_base(_Tp_alloc_type&& __a) noexcept
|
||
: _M_impl(std::move(__a)) { }
|
||
|
||
// 移动构造函数,只交换3个指针,不copy数据
|
||
_Vector_base(_Vector_base&& __x) noexcept
|
||
: _M_impl(std::move(__x._M_get_Tp_allocator()))
|
||
{ this->_M_impl._M_swap_data(__x._M_impl); }
|
||
|
||
_Vector_base(_Vector_base&& __x, const allocator_type& __a)
|
||
: _M_impl(__a)
|
||
{
|
||
if (__x.get_allocator() == __a)
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_swap_data(__x._M_impl);
|
||
else
|
||
{
|
||
size_t __n = __x._M_impl._M_finish - __x._M_impl._M_start;
|
||
_M_create_storage(__n);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
#endif
|
||
|
||
~_Vector_base()
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{
|
||
_M_deallocate(this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage
|
||
- this->_M_impl._M_start);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
_Vector_impl _M_impl;
|
||
|
||
pointer _M_allocate(size_t __n) {
|
||
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits <_Tp_alloc_type> _Tr;
|
||
return __n != 0 ? _Tr::allocate(_M_impl, __n) : 0; // 同_M_deallocate,一直往后调用的就是malloc函数
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
void _M_deallocate(pointer __p, size_t __n) {
|
||
typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits <_Tp_alloc_type> _Tr;
|
||
if (__p)
|
||
_Tr::deallocate(_M_impl, __p, __n); // 最后调用allocator_traits的deallocate,而该函数又是根据传递进来的_M_impl进行deallocate,一直往后,最后调用的就是free函数
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
private:
|
||
void _M_create_storage(size_t __n) {
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_start = this->_M_allocate(__n);
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_finish = this->_M_impl._M_start;
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage = this->_M_impl._M_start + __n;
|
||
}
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
小结:`_Vector_base`专门负责`vector`的内存管理,内部类`_M_impl`通过继承`_Tp_alloc_type`(也就是allocator)得到内存分配释放的功能,_M_allocate和_M_deallocate分别分配和释放vector所用内存,vector只需要负责元素构造和析构。
|
||
|
||
在vector中,默认内存分配器为`std::allocator<_Tp>`
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp>>
|
||
class vector : protected _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc> {
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
vector代码中使用基类的内存函数及typedef等:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp>>
|
||
class vector : protected _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc> {
|
||
typedef _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc> _Base;
|
||
typedef typename _Base::_Tp_alloc_type _Tp_alloc_type;
|
||
public:
|
||
typedef typename _Base::pointer pointer;
|
||
protected:
|
||
using _Base::_M_allocate;
|
||
using _Base::_M_deallocate;
|
||
using _Base::_M_impl;
|
||
using _Base::_M_get_Tp_allocator;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
## 2.vector迭代器
|
||
在vector中使用了两种迭代器,分别是正向`__normal_iterator`与反向迭代器`reverse_iterator`:
|
||
|
||
正向:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef __gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator <pointer, vector> iterator;
|
||
typedef __gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator <const_pointer, vector> const_iterator;
|
||
```
|
||
反向:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typedef std::reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
|
||
typedef std::reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
`__normal_iterator`与`reverse_iterator`都定义于stl_iterator.h,封装了vector元素的指针。
|
||
|
||
### 2.1 正向
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Iterator, typename _Container>
|
||
class __normal_iterator
|
||
{
|
||
protected:
|
||
_Iterator _M_current;
|
||
|
||
typedef iterator_traits<_Iterator> __traits_type;
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
typedef _Iterator iterator_type;
|
||
|
||
// iterator必须包含的五种typedef
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::iterator_category iterator_category;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::value_type value_type;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::difference_type difference_type;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::reference reference;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::pointer pointer;
|
||
|
||
_GLIBCXX_CONSTEXPR __normal_iterator() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
: _M_current(_Iterator()) { }
|
||
|
||
explicit
|
||
__normal_iterator(const _Iterator& __i) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
: _M_current(__i) { }
|
||
|
||
// Allow iterator to const_iterator conversion
|
||
template<typename _Iter>
|
||
__normal_iterator(const __normal_iterator<_Iter,
|
||
typename __enable_if<
|
||
(std::__are_same<_Iter, typename _Container::pointer>::__value),
|
||
_Container>::__type>& __i) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
: _M_current(__i.base()) { }
|
||
|
||
// Forward iterator requirements
|
||
reference
|
||
operator*() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return *_M_current; }
|
||
|
||
pointer
|
||
operator->() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return _M_current; }
|
||
|
||
// 前置++
|
||
__normal_iterator&
|
||
operator++() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{
|
||
++_M_current;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 后置++
|
||
__normal_iterator
|
||
operator++(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return __normal_iterator(_M_current++); }
|
||
|
||
// 前置--
|
||
// Bidirectional iterator requirements
|
||
__normal_iterator&
|
||
operator--() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{
|
||
--_M_current;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 后置--
|
||
__normal_iterator
|
||
operator--(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return __normal_iterator(_M_current--); }
|
||
|
||
// 随机访问迭代器都要重载[]操作符
|
||
// Random access iterator requirements
|
||
reference
|
||
operator[](difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return _M_current[__n]; }
|
||
|
||
// +=操作符 跳跃n个difference_type
|
||
__normal_iterator&
|
||
operator+=(difference_type __n) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ _M_current += __n; return *this; }
|
||
|
||
// +操作符 跳跃n个difference_type
|
||
__normal_iterator
|
||
operator+(difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return __normal_iterator(_M_current + __n); }
|
||
|
||
// -=操作符 后退n个difference_type
|
||
__normal_iterator&
|
||
operator-=(difference_type __n) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ _M_current -= __n; return *this; }
|
||
|
||
// -操作符 后退n个difference_type
|
||
__normal_iterator
|
||
operator-(difference_type __n) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return __normal_iterator(_M_current - __n); }
|
||
|
||
const _Iterator&
|
||
base() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return _M_current; }
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
_M_current是指向迭代器位置的指针,这是一个随机访问型指针,operator+和operator-等移动操作可以直接移动到目的地,非随机访问型指针只能一步步移动。
|
||
|
||
### 2.2 反向
|
||
|
||
|
||
vector还会使用reverse_iterator,即逆序迭代器,顾名思义,其移动方向与普通迭代器相反
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Iterator>
|
||
class reverse_iterator
|
||
: public iterator<typename iterator_traits<_Iterator>::iterator_category,
|
||
typename iterator_traits<_Iterator>::value_type,
|
||
typename iterator_traits<_Iterator>::difference_type,
|
||
typename iterator_traits<_Iterator>::pointer,
|
||
typename iterator_traits<_Iterator>::reference>
|
||
{
|
||
protected:
|
||
_Iterator current;
|
||
|
||
typedef iterator_traits<_Iterator> __traits_type;
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
typedef _Iterator iterator_type;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::difference_type difference_type;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::pointer pointer;
|
||
typedef typename __traits_type::reference reference;
|
||
|
||
// 省略不重要的代码
|
||
|
||
|
||
// 该迭代器是从后面end()开始,需要往前一步,才可以获取到有效的迭代器位置
|
||
reference
|
||
operator*() const
|
||
{
|
||
_Iterator __tmp = current;
|
||
return *--__tmp;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 通过调用上述*操作符直接实现
|
||
pointer
|
||
operator->() const
|
||
{ return &(operator*()); }
|
||
|
||
|
||
// 前置++操作符完成后退任务
|
||
reverse_iterator&
|
||
operator++()
|
||
{
|
||
--current;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 后置++
|
||
reverse_iterator
|
||
operator++(int)
|
||
{
|
||
reverse_iterator __tmp = *this;
|
||
--current;
|
||
return __tmp;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 前置--操作符完成前进任务
|
||
reverse_iterator&
|
||
operator--()
|
||
{
|
||
++current;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 后置--
|
||
reverse_iterator
|
||
operator--(int)
|
||
{
|
||
reverse_iterator __tmp = *this;
|
||
++current;
|
||
return __tmp;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// +操作符
|
||
reverse_iterator
|
||
operator+(difference_type __n) const
|
||
{ return reverse_iterator(current - __n); }
|
||
|
||
// +=操作符
|
||
reverse_iterator&
|
||
operator+=(difference_type __n)
|
||
{
|
||
current -= __n;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// -操作符
|
||
reverse_iterator
|
||
operator-(difference_type __n) const
|
||
{ return reverse_iterator(current + __n); }
|
||
|
||
// -=操作符
|
||
reverse_iterator&
|
||
operator-=(difference_type __n)
|
||
{
|
||
current += __n;
|
||
return *this;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// []操作符
|
||
reference
|
||
operator[](difference_type __n) const
|
||
{ return *(*this + __n); }
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 3.vector的数据结构
|
||
|
||
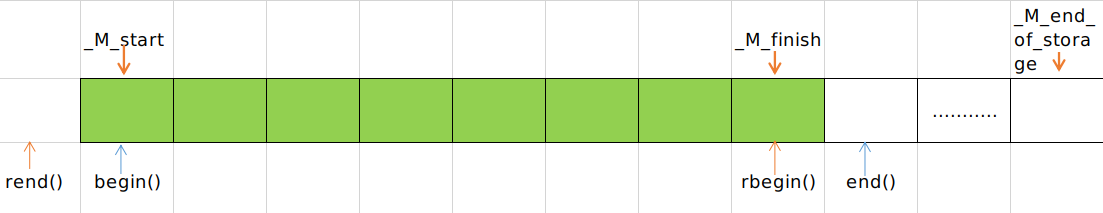
vector内存由_M_impl中的M_start,_M_finish,_M_end_of_storage三个指针管理,所有关于地址,容量大小等操作都需要用到这三个指针:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
iterator begin() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_start); }
|
||
iterator end() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_finish); }
|
||
reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept
|
||
{ return reverse_iterator(end()); }
|
||
reverse_iterator rend() noexcept
|
||
{ return reverse_iterator(begin()); }
|
||
size_type size() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return size_type(this->_M_impl._M_finish - this->_M_impl._M_start); }
|
||
size_type capacity() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return size_type(this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage - this->_M_impl._M_start); }
|
||
bool empty() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ return begin() == end(); }
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
_M_finish和_M_end_of_storage之间的空间没有数据,有时候这是一种浪费,c++11提供了一个很有用的函数shrink_to_fit(),将这段未使用空间释放,主要调用了下面代码,
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Alloc>
|
||
bool vector<bool, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_shrink_to_fit()
|
||
{
|
||
if (capacity() - size() < int(_S_word_bit)) // 64位系统为64bytes
|
||
return false;
|
||
__try
|
||
{
|
||
_M_reallocate(size());
|
||
return true;
|
||
}
|
||
__catch(...)
|
||
{
|
||
return false;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Alloc>
|
||
void vector<bool, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_reallocate(size_type __n)
|
||
{
|
||
_Bit_type* __q = this->_M_allocate(__n);
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_finish = _M_copy_aligned(begin(), end(),
|
||
iterator(__q, 0));
|
||
this->_M_deallocate();
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_start = iterator(__q, 0);
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage = __q + _S_nword(__n);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
而`_M_copy_aligned`通过两个std::copy实现:
|
||
|
||
第一次swap把`__first`的指针与`__last`的指针之间的数据拷贝到`__result`指针所指向的起始位置。
|
||
第二次swap获得`__last`的指针对应的迭代器。
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
iterator
|
||
_M_copy_aligned(const_iterator __first, const_iterator __last,
|
||
iterator __result)
|
||
{
|
||
// _Bit_type * _M_p; _Bit_type为unsigned long类型
|
||
_Bit_type* __q = std::copy(__first._M_p, __last._M_p, __result._M_p);
|
||
return std::copy(const_iterator(__last._M_p, 0), __last,
|
||
iterator(__q, 0));
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
先分配size()大小的内存空间,用于存储`begin()`与`end()`之间的数据,释放原来的vector空间,新的vector只包含size()数量的数据,并修改`_M_start`与`_M_end_of_storage`指向。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 4.vector构造与析构
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
//使用默认内存分配器
|
||
vector() : _Base() { }
|
||
//指定内存分配器
|
||
explicit vector(const allocator_type& __a) : _Base(__a) { }
|
||
//初始化为n个__value值,如果没指定就使用该类型默认值
|
||
explicit vector(size_type __n, const value_type& __value = value_type(),
|
||
const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _Base(__n, __a)
|
||
{ _M_fill_initialize(__n, __value); }
|
||
//拷贝构造函数
|
||
vector(const vector& __x)
|
||
: _Base(__x.size(),
|
||
_Alloc_traits::_S_select_on_copy(__x._M_get_Tp_allocator()))
|
||
{ this->_M_impl._M_finish =
|
||
std::__uninitialized_copy_a(__x.begin(), __x.end(),
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_start,
|
||
_M_get_Tp_allocator());
|
||
}
|
||
//c++11的移动构造函数,获取__x的M_start,_M_finish,_M_end_of_storage,并不需要数据拷贝
|
||
vector(vector&& ) noexcept
|
||
: _Base(std::move(__x)) { }
|
||
//从list中拷贝数据,也是c++11才有的
|
||
vector(initializer_list<value_type> __l,
|
||
const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type())
|
||
: _Base(__a)
|
||
{
|
||
_M_range_initialize(__l.begin(), __l.end(), random_access_iterator_tag());
|
||
}
|
||
//支持vector使用两个迭代器范围内的值初始化,除了stl的迭代器,也可以是数组地址
|
||
template<typename _InputIterator,
|
||
typename = std::_RequireInputIter<_InputIterator>>
|
||
vector(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last,
|
||
const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type())
|
||
: _Base(__a)
|
||
{ _M_initialize_dispatch(__first, __last, __false_type()); }
|
||
//只析构所有元素,释放内存由vector_base完成
|
||
~vector() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
|
||
{ std::_Destroy(this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_finish,_M_get_Tp_allocator()); }
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## 5.vector
|
||
|
||
插入涉及到内存分配,动态调整,与一开始提到的vector与array区别,就在下面体现出:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typename vector<_Tp, _Alloc>::iterator
|
||
vector<_Tp, _Alloc>::insert(iterator __position, const value_type& __x)
|
||
{
|
||
const size_type __n = __position – begin();
|
||
//插入到最后一个位置,相当于push_back
|
||
if (this->_M_impl._M_finish != this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage
|
||
&& __position == end())
|
||
{
|
||
_Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl, this->_M_impl._M_finish, __x);
|
||
++this->_M_impl._M_finish;
|
||
}
|
||
else
|
||
{
|
||
_M_insert_aux(__position, __x);
|
||
}
|
||
return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_start + __n);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
其中`_M_insert_aux`实现:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc>
|
||
void vector<_Tp, _Alloc>::_M_insert_aux(iterator __position, const _Tp& __x)
|
||
{
|
||
//内存空间足够
|
||
if (this->_M_impl._M_finish != this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage)
|
||
{
|
||
_Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl, this->_M_impl._M_finish,
|
||
_GLIBCXX_MOVE(*(this->_M_impl._M_finish
|
||
- 1)));
|
||
++this->_M_impl._M_finish;
|
||
//__position后的元素依次向后移动一个位置
|
||
_GLIBCXX_MOVE_BACKWARD3(__position.base(),
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_finish - 2,
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_finish – 1);
|
||
//目标地址赋值
|
||
*__position = _Tp(std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
|
||
}
|
||
else
|
||
{
|
||
//内存加倍
|
||
const size_type __len =
|
||
_M_check_len(size_type(1), "vector::_M_insert_aux");
|
||
const size_type __elems_before = __position - begin();
|
||
pointer __new_start(this->_M_allocate(__len));
|
||
pointer __new_finish(__new_start);
|
||
__try
|
||
{
|
||
//给position位置赋值
|
||
_Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl,
|
||
__new_start + __elems_before,
|
||
std::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
|
||
__x);
|
||
__new_finish = 0;
|
||
//拷贝position位置前元素
|
||
__new_finish = std::__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a
|
||
(this->_M_impl._M_start, __position.base(),
|
||
__new_start, _M_get_Tp_allocator());
|
||
|
||
++__new_finish;
|
||
//拷贝position位置后元素
|
||
__new_finish
|
||
= std::__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a
|
||
(__position.base(), this->_M_impl._M_finish,
|
||
__new_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator());
|
||
}
|
||
__catch(...)
|
||
{
|
||
if (!__new_finish)
|
||
_Alloc_traits::destroy(this->_M_impl,
|
||
__new_start + __elems_before);
|
||
else
|
||
std::_Destroy(__new_start, __new_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator());
|
||
_M_deallocate(__new_start, __len);
|
||
__throw_exception_again;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
//析构原vector所有元素
|
||
std::_Destroy(this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_finish,
|
||
_M_get_Tp_allocator());
|
||
//释放原vector内存空间
|
||
_M_deallocate(this->_M_impl._M_start,
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage,this->_M_impl._M_start);
|
||
//vector内存地址指向新空间
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_start = __new_start;
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_finish = __new_finish;
|
||
this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage = __new_start + __len;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
其中`_M_check_len`:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
|
||
size_type
|
||
_M_check_len(size_type __n, const char* __s) const
|
||
{
|
||
if (max_size() - size() < __n)
|
||
__throw_length_error(__N(__s));
|
||
|
||
const size_type __len = size() + std::max(size(), __n); //如果n小于当前size,内存加倍,否则内存增长n。
|
||
return (__len < size() || __len > max_size()) ? max_size() : __len;
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
内存分配策略并不是简单的加倍,如果n小于当前size,内存加倍,否则内存增长n。
|
||
|
||
|
||
学习资料:
|
||
> 侯捷《STL源码剖析》
|
||
|
||
> https://www.cnblogs.com/coderkian/p/3888429.html |