215 lines
7.6 KiB
Markdown
215 lines
7.6 KiB
Markdown
|
||
# STL之set与multiset那些事
|
||
set/multiset以rb_tree为底层结构,因此有元素自动排序特性。排序的依据是key,而set/multiset元素的value和key合二为一:value就是key。
|
||
|
||
|
||
我们无法使用set/multiset的iterators改变元素值(因为key有其严谨排列规则)。
|
||
set/multiset的iterator是其底部RB tree的const-iterator,就是为了禁止用户对元素赋值。
|
||
|
||
set元素的key必须独一无二,因此其insert使用的是rb_tree的`_M_insert_unique()`,而multiset元素的key可以重复,因此其insert使用的是rb_tree的`_M_insert_equal()`。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 1.set
|
||
|
||
针对set源码比较简单,故从下面几个问题出发。
|
||
|
||
|
||
> 第一个问题:key是value,value也是key。
|
||
|
||
|
||
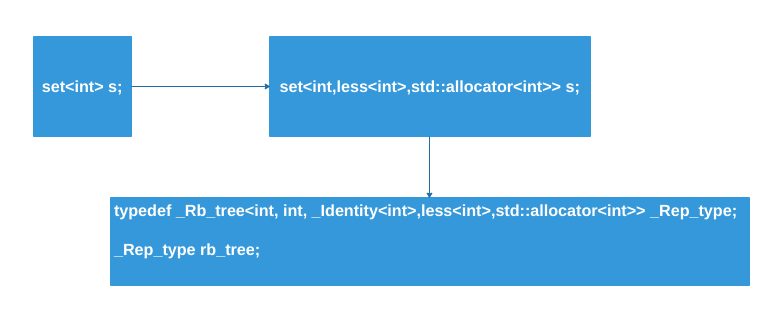
具体代码再第二个问题中会有,这里给出我们通常写代码后内部逻辑,我们看到里面有个红黑树,而红黑树的定义key与value是一样的,所以回答了这个问题。(源码中typedef都是来自key)。
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,
|
||
typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >
|
||
class set
|
||
{
|
||
// concept requirements
|
||
typedef typename _Alloc::value_type _Alloc_value_type;
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
// typedefs:
|
||
//@{
|
||
/// Public typedefs.
|
||
typedef _Key key_type;
|
||
typedef _Key value_type; // value也是key
|
||
typedef _Compare key_compare;
|
||
typedef _Compare value_compare;
|
||
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
|
||
//@}
|
||
|
||
private:
|
||
|
||
typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Identity<value_type>,
|
||
key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
|
||
_Rep_type _M_t; // Red-black tree representing set.
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
> 第二个问题:无法使用迭代器改变元素值。
|
||
|
||
无法使用迭代器改变元素值我们看后面迭代器,发现全部用的是`const_iterator`,所以第二个问题也回答完毕。
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,
|
||
typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Key> >
|
||
class set
|
||
{
|
||
private:
|
||
|
||
typedef _Rb_tree<key_type, value_type, _Identity<value_type>,
|
||
key_compare, _Key_alloc_type> _Rep_type;
|
||
_Rep_type _M_t; // Red-black tree representing set.
|
||
|
||
public:
|
||
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator iterator;
|
||
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;
|
||
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator reverse_iterator;
|
||
typedef typename _Rep_type::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator;
|
||
};
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
经过前面分析,让我们想起了queue、priority_queue、stack,他们都使用的是底层的容器,所以称为容器适配器,而set也是使用底层的容器,所以也可以被称为container adapter,即容器适配器。
|
||
|
||
> 第三个问题:插入是唯一的key。
|
||
|
||
底部调用的是`_M_insert_unique`。
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _InputIterator>
|
||
set(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last)
|
||
: _M_t()
|
||
{ _M_t._M_insert_unique(__first, __last); }
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们来简单看一下这个函数实现:
|
||
下面`_M_get_insert_unique_pos`返回的是个pair,如果插入的key相同则pair的second为0,根据是否为0可以判断是否key重复,在下面代码中判断时候,当second不为0,也就是不重复的时候,那么就可以直接插入,此时直接构造一个second为true的pair,否则构造一个second为false的pair。
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Key, typename _Val, typename _KeyOfValue,
|
||
typename _Compare, typename _Alloc>
|
||
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
|
||
template<typename _Arg>
|
||
#endif
|
||
pair<typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue,
|
||
_Compare, _Alloc>::iterator, bool>
|
||
_Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue, _Compare, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_insert_unique( _Arg && __v )
|
||
|
||
{
|
||
typedef pair<iterator, bool> _Res;
|
||
pair<_Base_ptr, _Base_ptr> __res
|
||
= _M_get_insert_unique_pos( _KeyOfValue() ( __v ) );
|
||
|
||
if ( __res.second )
|
||
return(_Res( _M_insert_( __res.first, __res.second,
|
||
_GLIBCXX_FORWARD( _Arg, __v ) ),
|
||
true ) );
|
||
|
||
return(_Res( iterator( static_cast<_Link_type>(__res.first) ), false ) );
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们再看看上面提到的函数:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Key, typename _Val, typename _KeyOfValue,typename _Compare, typename _Alloc>
|
||
pair<typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue,
|
||
_Compare, _Alloc>::_Base_ptr,typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue,Compare, _Alloc>::_Base_ptr>
|
||
_Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue, _Compare, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_get_insert_unique_pos(const key_type& __k)
|
||
{
|
||
// typedef pair
|
||
typedef pair<_Base_ptr, _Base_ptr> _Res;
|
||
// _x表示当前节点,_y表示_x的父节点
|
||
_Link_type __x = _M_begin();
|
||
_Link_type __y = _M_end();
|
||
bool __comp = true;
|
||
|
||
// 寻找插入点
|
||
while (__x != 0)
|
||
{
|
||
__y = __x;
|
||
// __k<__x是否为true
|
||
__comp = _M_impl._M_key_compare(__k, _S_key(__x));
|
||
// __k<__x就往左孩子查找,否则右孩子查找
|
||
__x = __comp ? _S_left(__x) : _S_right(__x);
|
||
}
|
||
iterator __j = iterator(__y);
|
||
// __k<__y,往__y的左孩子插入节点即可,不是做插入,是找到位置即可。
|
||
if (__comp)
|
||
{
|
||
// 特殊位置
|
||
if (__j == begin())
|
||
return _Res(__x, __y);
|
||
else
|
||
--__j; // 左孩子 这里调用了--操作符
|
||
}
|
||
// __j<__k,返回当前节(__x=0)点与父节点
|
||
if (_M_impl._M_key_compare(_S_key(__j._M_node), __k))
|
||
return _Res(__x, __y);
|
||
// _j>=__k,插入失败
|
||
return _Res(__j._M_node, 0);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
上述pair的使用给了我一个启发,竟然可以这样用,那么我们来学习一下:
|
||
```cpp
|
||
cout<<"flag: "<<itree._M_insert_unique(5).second<<endl; // 学习返回值
|
||
typedef pair<int ,bool> _Res; // 也来用一下typedef后的pair
|
||
cout<<_Res(1,true).first<<endl; // 直接包裹
|
||
_Res r=make_pair(2,false); // 定义新对象
|
||
cout<<r.first<<endl; // 输出结果
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 2.multiset
|
||
同理,multiset与set定义基本类似,不同之处,在于插入使用的是另一个函数,这样才使它能够完成重复key的插入!
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _InputIterator>
|
||
multiset(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last)
|
||
: _M_t()
|
||
{ _M_t._M_insert_equal(__first, __last); }
|
||
```
|
||
下面来分析一下`_M_insert_equal`:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue, _Compare, _Alloc>::iterator
|
||
_Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue, _Compare, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_insert_equal(_Arg&& __v)
|
||
{
|
||
pair<_Base_ptr, _Base_ptr> __res = _M_get_insert_equal_pos(_KeyOfValue()(__v));
|
||
return _M_insert_(__res.first, __res.second, _GLIBCXX_FORWARD(_Arg, __v));
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们继续追踪上述的`_M_get_insert_equal_pos`函数:
|
||
|
||
```cpp
|
||
template<typename _Key, typename _Val, typename _KeyOfValue,
|
||
typename _Compare, typename _Alloc>
|
||
pair<typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue,
|
||
_Compare, _Alloc>::_Base_ptr,
|
||
typename _Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue,
|
||
_Compare, _Alloc>::_Base_ptr>
|
||
_Rb_tree<_Key, _Val, _KeyOfValue, _Compare, _Alloc>::
|
||
_M_get_insert_equal_pos(const key_type& __k)
|
||
{
|
||
typedef pair<_Base_ptr, _Base_ptr> _Res;
|
||
_Link_type __x = _M_begin();
|
||
_Link_type __y = _M_end();
|
||
while (__x != 0)
|
||
{
|
||
__y = __x;
|
||
__x = _M_impl._M_key_compare(__k, _S_key(__x)) ?
|
||
_S_left(__x) : _S_right(__x);
|
||
}
|
||
return _Res(__x, __y);
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
我们对比multiset与set的这几个函数发现,返回的pair有着显著的差异,之前的set需要返回最终是否插入成功,因为key不可重复,而multiset不需要返回是否插入成功,所以pair中不存在bool类型,故它是直接返回的插入点所构成的pair,因此,与之前相比较而言,不管你有多少个key,重复如何,都可以插入进去。
|
||
|